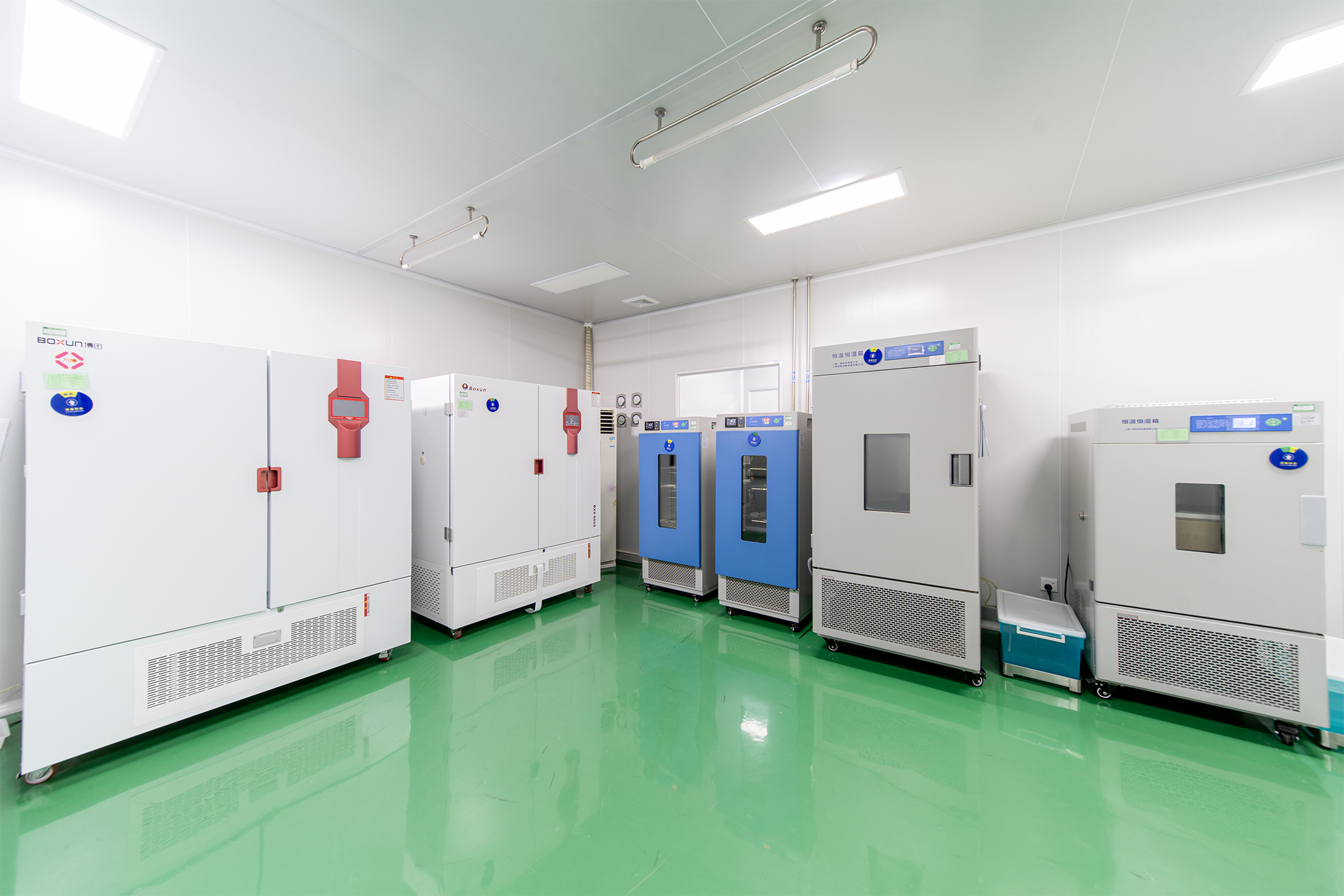
Guangzhou MedClear Testing Technology Services Co., Ltd. is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Guangzhou MedClear Medical Device Services Co., Ltd. The testing fields include medical devices, medical device packaging, cleanrooms (areas), cosmetics, food, and other sanitary products.The test items include microbiological test, ethylene oxide residue test, cleanrooms test, and sterile barrier system test, etc. The company is committed to providing accurate, credible, professional, and efficient testing services. The company has obtained CNAS certificate issued by China National Accreditation Service for Conformity Assessment and CMA certificate issued by Guangdong Administration for Market Regulation.
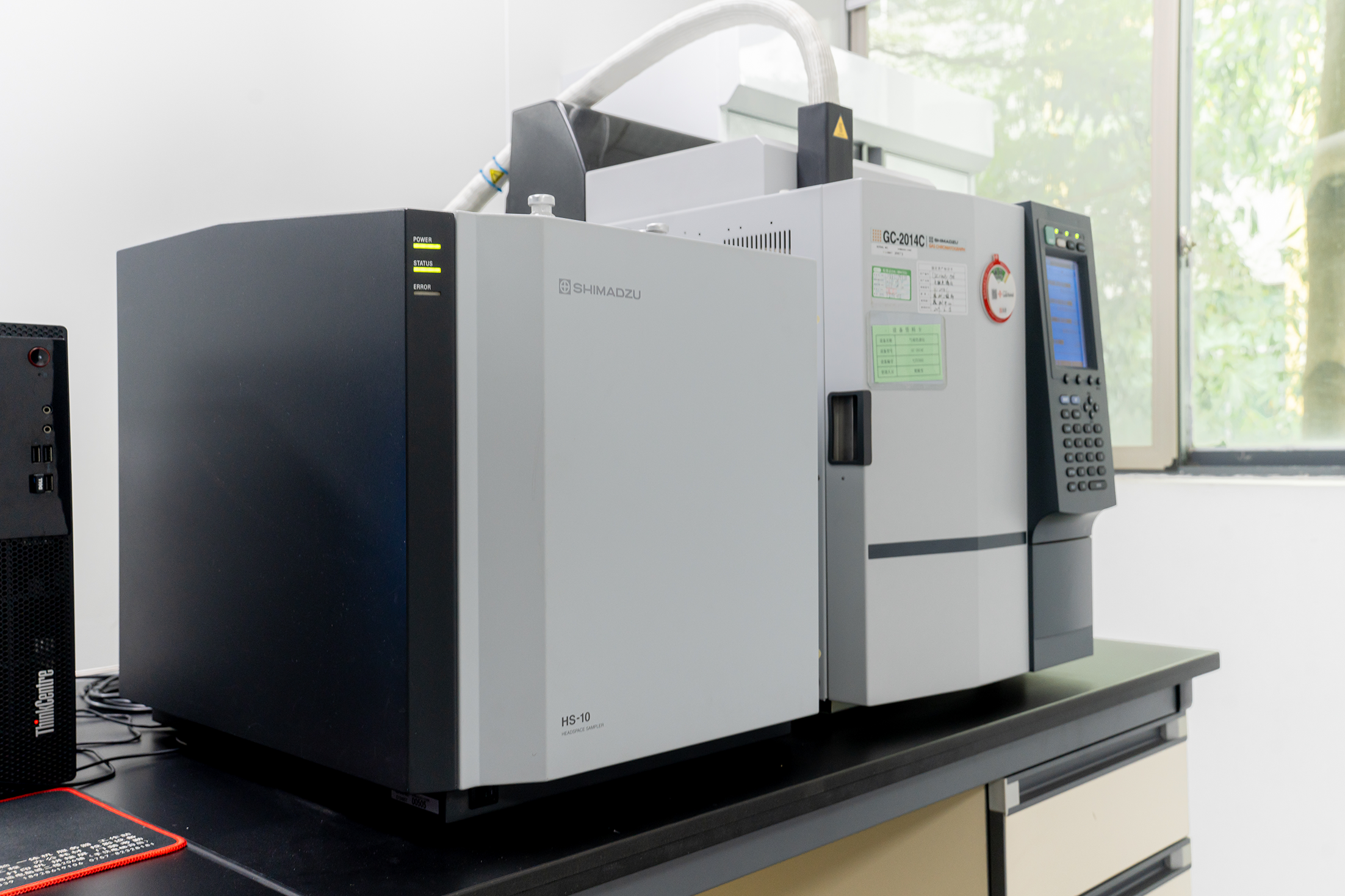




| Testing Domain | Testing Item | Standard or Method |
| Medical Devices | Sterility Testing | GB/T 14233.2-2005 Test methods for infusion, transfusion, injection equipment for medical use— Part 2: Biological |
| GB/T 19973.2-2025 Sterilization of medical devices—Microbiological methods—Part 2: Tests of sterility performed in the definition,validation and maintenance of a sterilization process | ||
| ISO11737-2:2019 Sterilization of health care products-Microbiological methods- Part2:Tests of sterility performed in the definition,validation and maintenance of a sterilization process | ||
| Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025 edition) 4 General Rules 1101 | ||
| General Rule 71 of U.S. Pharmacopeia-National Formulary, effective 2022 | ||
| European Pharmacopoeia version 11.0, version 2.6.1 | ||
| Microbiological Limit Testing | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025 edition) General Rules 1105/1106 | |
| General Rule 61 of U.S Pharmacopeia-National Formulary, effective 2022 | ||
| European Pharmacopoeia version 11.0 2.6.12 | ||
| ISO11737-1:2018 Sterilization of health care products-Microbiological methods- Part1:Determination of a population of microorganisms on products | ||
| GB/T 19973.1-2023 Sterilization of medical devices — Microbiological methods— Part 1:Estimation of population of microorganisms on the products | ||
| Bacterial Endotoxin | GB/T 14233.2-2005 Test methods for infusion ,transfusion ,injection equipment for medical use— Part 2 : Biological test methods | |
| Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025 edition) 4 General Rules 1143 | ||
| General Rule 85 of U.S. Pharmacopeia-National Formulary, effective 2022 | ||
| YY/T 0618-2017 Test methods for bacterial endotoxins of medical devices— Routine monitoring and alternatives to batch testing | ||
| ANSI/AAMI ST72:2019 Bacterial endotoxins-Test methods,routine monitoring,and alternatives to batch testing | ||
| ISO 11737-3:2023 Sterilization of health care products-Microbiological methods- Park3 Bacterial endotoxin testing | ||
| Ethylene Oxide Residue | GB/T 14233.1-2022 Test methods for medical infusion, blood transfusion and injection apparatus - Part 1: Chemical analysis methods | |
| GB/T 16886.7-2015 Biological evaluation of medical devices- Part 7: Ethylene oxide sterilization residuals | ||
| ISO 10993-7:2008/Amd1:2019 Biological evaluation of medical devices-Part7:Ethylene oxide sterilization residuals | ||
| Chloroethanol (2-Chloroethanol) Content | GB/T 16886.7-2015 Biological evaluation of medical devices- Part 7: Ethylene oxide sterilization residuals | |
| ISO 10993-7:2008/Amd1:2019 Biological evaluation of medical devices-Part7:Ethylene oxide sterilization residuals |
| Testing Domain | Testing Item | Standard or Method |
| Medical Device Packaging | Accelerated Aging | YY/T 0681.1-2018 Test methods for sterile medical device package- Part 1:Test guide for accelerated aging |
| ASTM F1980-2021 Standard Guide for Accelerated Aging of Sterile Barrier Systems for Medical Deviced | ||
| Seal Leakage | YY/T 0681.4-2021 Test methods for sterile medical device package- Part 4:Detecting seal leaks in porous packages by dye penetration | |
| ASTM F1929-2023 Standard Test Method for Detecting Seal Leaks in Porous Medical Packaging by Dye Penetration | ||
| Seal Strength | YY/T 0681.2-2010 Test methods for sterile medical device package- Part 2 :Seal strength of flexible battier materials | |
| ASTM F88/F88M-2023 Standard Test Method for Seal Strength of Flexible Barrier Materials | ||
| Seal Integrity | YY/T 0681.11-2014 Test methods for sterile medical device package- Part 11:Determining integrity of seals for medical packaging by visual inspection | |
| ASTM F1886/F1886M-2016 Standard Test Method for Determining Integrity of Seals for Flexible Packaging by Visual Inspection | ||
Internal pressurization failure resistance of unrestrained packages | YY/T 0681.3-2010 Test methods for sterile medical device package- Part 3: Internal pressurization failure resistance of unrestrained packages | |
| ASTM F1140 F1140M-13(Reapproved2020) Standard Test Methods for Internal Pressurization Failure Resistance of Unrestrained Packages | ||
Detection of coarse leakage by internal pressure method (bubble method) | YY/T 0681.5-2010 Test methods for sterile medical device package-Part 5 : Detecting gross leaks in medical packaging by internal pressurization (bubble test) | |
| ASTM F2096-11(Reapproved 2019) Standard Test Methods for Detecting Gross Leaks in Packaging by Internal Pressurizationg(Bubble Test) |
| Testing Domain | Testing Item | Standard or Method |
Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | Microbiological Limit Testing | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025 edition) General Rules 1105/1106 |
| Sterility testing | Chinese Pharmacopoeia (2025 edition) 4 General Rules 1101 |
| Testing Domain | Testing Item | Standard or Method |
| Cleanrooms (Areas) | Temperature/Relative Humidity | Appendix E.5 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| Appendix C.6/C.7 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| Appendix B.8/B.9 of GB/T25915.3-2024 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments— Part 3:Test methods | ||
| ISO 14644-3:2019 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments-Part 3:Test methods | ||
| YBB00412004-2015 Test for Clean Rooms(Areas)Producing Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Air Volume | GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Wind speed | Appendix E.1 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Appendix C.2 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| Appendix B.4 of GB/T 25915.3-2024 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments— Part 3:Test methods | ||
| ISO 14644-3:2019 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments-Part 3:Test methods | ||
| Cross section mean wind speed | YBB00412004-2015 Test for Clean Rooms (Areas) Producing Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | |
| Air change rate | Appendix E.1 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| Appendix B.4 of GB/T 25915.3-2024 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments- Part 3: Test methods | ||
| ISO 14644-3:2019 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments-Part 3:Test methods | ||
| YBB00412004-2015 Test for Clean Rooms(Areas)Producing Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Static pressure difference | Appendix E.2 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| Appendix C.3 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| Appendix B.5 of GB/T25915.3-2024 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments— Part 3 :Test methods | ||
| ISO 14644-3:2019 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments-Part 3:Test methods | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Concentration of suspended particles | Appendix E.4 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| Appendix B.1 of GB/T25915.3-2010 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments— Part 3:Test methods | ||
| GB/T 16292-2010 Test method for airborne particles in clean room(zone)of the pharmaceutical industry | ||
| Appendix C.1 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| Appendix A of GB/T25915.1-2021 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments-Part 1:Classification of air cleanliness by particle concentration | ||
| ISO 14644-1:2015 Cleanrooms and associated controlled environments-Part 1:Classification of air cleanliness by particle concentration | ||
| YBB00412004-2015 Test for Clean Rooms(Areas)Producing Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Settling microbe | Appendix E8 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| GB/T 16294-2010 Test method for setting microbe in clean room(zone)of the pharmaceutical industy | ||
| YBB00412004-2015 Test for Clean Rooms(Areas)Producing Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Appendix C.16 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| Airborne microbe | Appendix E.8 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB/T 16293-2010 Test method for airborne microbe in clean room(zone)of the pharmaceutical industry | ||
| Appendix C.16 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| YBB00412004-2015 Test for Clean Rooms(Areas)Producing Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Illuminance | Appendix E.7 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| Appendix C.10 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| YBB00412004-2015 Test for Clean Rooms(Areas)Producing Pharmaceutical Packaging Materials | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room | ||
| Noise | Appendix E.6 of GB 50591-2010 Code for construction and acceptance of cleanroom | |
| GB 50333-2013 Architectural technical code for hospital clean operating department | ||
| Appendix C.9 of GB51110-2015 Code of construction and quality acceptance of industrial cleanroom | ||
| GB 50073-2013 Code for design of clean room |
| Testing Domain | Testing Item | Standard or Method |
| Cosmetics | Total colonies | "Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics" (2015 edition) Chapter 5 2 |
| "Standard test Methods for Microbiology of Cosmetics - Determination of Total Bacterial Colonies" GB 7918.2-1987 | ||
| Moulds and yeasts | "Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics" (2015 edition) Chapter 5 6 | |
| Thermotolerant coliforms | "Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics" (2015 edition) Chapter 5 3 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | "Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics" (2015 edition) Chapter 5 4 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | "Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics" (2015 edition) Chapter 5 | |
| Ethylene Oxide | "Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics" (2015 edition) Chapter 4 2.21 | |
| Methyl ethylene oxide |
| Testing Domain | Testing Item | Standard or Method |
| Disposable Sanitary Products | Total bacterial colonies | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B2 |
| Initial contaminating bacteria | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B2 | |
| Coliform bacteria | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B3 | |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B4 | |
| Staphylococcus aureus | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B5 | |
| Hemolytic streptococci | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B6 | |
| Total fungal colonies | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B7 | |
| Characterization of fungi | "Hygienic standard for disposable sanitary products" GB 15979-2024 Appendix B8 |
| Testing Domain | Testing Item | Standard or Method |
| Food | Total number of bacteria | GB 4789.2-2022 Microbiological examination of food determination of total colonies |
| Moulds and yeasts | GB 4789.15-2016 National Food Safety Standard Food Microbiological Examination Mold and Yeast Count | |
| Coliform bacteria | GB 4789.3-2016 National Food Safety Standard Food Microbiology Determination Coliform Bacteria Count | |
| Staphylococcus Aureus | GB 4789.10-2016 National standard for food safety microbiological examination of Staphylococcus aureus |
| Radiation Sterilization Dose Setting | ||
| Introduction | Irradiation sterilization is an effective method to kill most microorganisms on substances using electromagnetic waves generated by ionizing radiation. The radiation used for sterilization includes electron beams, X-rays and gamma rays. All of them can control microbial growth or kill microorganisms in specific ways. X-rays and gamma rays can oxidize other substances or produce free radicals (OH·H) and then act on biological molecules, or directly act on biological molecules, break hydrogen bonds, oxidize double bonds, destroy ring structures or polymerize some molecules, and destroy and change the structure of biological macromolecules, thereby inhibiting or killing microorganisms. | |
| Radiation sterilization dose setting Relevant standards | ISO 11137-2:2013/GB18280.2-2015 Sterilization of health care products-Radiation - Part 2: Establishment of sterilization dose ISO 11737-1:2018 Microbiological methods for sterilization of medical devices - Part 1: Determination of the total number of microorganisms on a product ISO 11737-1:2019 Microbiological methods for sterilization of medical devices - Part 2: Sterility tests for definition, validation and maintenance of the sterilization process | |
| Radiation sterilization service scope | Medical devices, drugs, cosmetics, food, packaging materials, toys, etc. | |

1 Fill out the commission form
2 Sample provision (on-site delivery, mailing, on-site sampling)
1 Review and confirmation of the commission form
2 Sample confirmation and receipt
1 Sample registration
2 Laboratory receives samples, conducts tests, and issues a test report
3 Sample handling (including test residual samples, retention, etc.)
Issue the test report after receiving the testing fee

Guangzhou MedClear has deep expertise in the field of sterile medical device testing. With extensive practical experience in microbiological testing, ethylene oxide residue testing, cleanrooms testing, sterile barrier system testing, and testing equipment validation.The company has conducted several training courses related to sterile medical device testing. The training topics cover a wide range of knowledge, including basic microbiology, bioburden test, cleanrooms test, and ethylene oxide residue test, etc. These courses help inspectors fully and accurately understand the latest regulatory standards and requirements, master the corresponding testing technologies for sterile medical devices, and enhance the company's own inspection capabilities. Combining theoretical knowledge with practical operations, trainees who pass the assessment successfully will be awarded a certificate of training completion.

To maintain the integrity, independence, and impartiality of our company's inspection work, and to continuously meet the requirements of CNAS-CL01:2018(ISO/IEC 17025:2017), RB/T214-2017, as well as related accreditation requirements and laws and regulations, we provide our clients with accurate, credible, professional,and efficient testing and analytical services. We hereby make the following statement of integrity:
Our company and its personnel adhere to the relevant national laws and regulations, conducting inspection and testing activities objectively, independently, fairly, justly, and honestly, upholding professional ethics, and taking social responsibility.
Our company maintains a scientific and impartial attitude towards all commissioned inspections. The inspectors carry out their work independently, free from external pressures, and resolutely resist any actions that compromise the fairness of the testing and analysis work. Our management commits to not interfering inappropriately with the testing and analysis work, ensuring its fairness and independence.
Our company continuously improves and perfects the quality management system for testing and inspection, strictly implementing current technical standards and normative requirements to ensure that testing and inspection data are truthful, objective, and accurate, and not issuing any false testing or inspection reports.
Our company adheres to professional standards and issues testing and inspection reports within the scope of competence specified by the accreditation certificate, according to the procedures and requirements set by relevant standards or technical specifications.
Our company ensures strict confidentiality of the technical materials, drawings, and data of our clients, effectively protecting their confidential information and proprietary rights.
Our company is responsible for the truthfulness of this statement of integrity and accepts supervision and complaints from the public.
Guangzhou MedClear Testing Technology Services Co., Ltd.